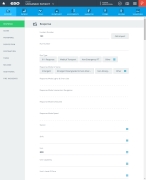
Spinal immobilization screening tool
Spinal immobilization is performed to prevent or minimize secondary damage to the spinal cord if instability of the spinal column is suspected. It typically involves the use of a number of devices and strategies to stabilize the spinal column after injury, and thereby prevent spinal cord damage. The practice is widely used in trauma patients with suspected spinal cord injury in the pre-hospital setting. You can evaluate the need for spinal immobilization with the patient by screening them for specific indicators of neck and spinal injury.
-
 (If you have not done so already) Access the EHR module in the ESO Suite.
(If you have not done so already) Access the EHR module in the ESO Suite.
-
Do one of the following.
-
(If you are already working in the ESO Suite) Click the Home icon in the upper left corner of the screen.
-
 (If you have not yet logged in) Log in to the ESO Suite.
(If you have not yet logged in) Log in to the ESO Suite.
-
In a web browser, go to https://www.esosuite.net/EsoSuite.
The ESO Suite login screen appears.
-
Enter your user name, password, and agency name, then click Let's Go.
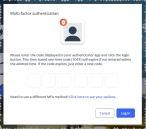
If MFA is enabled, the Multi-factor authentication dialog box appears, displaying one or more methods you can use to verify your login credentials. The number of methods that appear in the dialog box depends on what MFA methods your ESO Suite administrators enabled in the Admin module.

Click graphics
to open them.Information on enabling MFA and specific MFA methods is available in the Admin module online help, in Configure multiple-factor authentication.
Note: If your ESO Suite administrators have disabled MFA ("opted-out"), this dialog does not appear.
-
(If the Multi-factor authentication dialog box appears) Depending on which buttons appear in the dialog box, verify your login in one of the following ways.
 With an authenticator application.
With an authenticator application.
-
Click MFA verification via authenticator app.
The dialog box updates with boxes for entering the numbers of the authentication code, and the ESO Suite sends an authentication code to the authenticator application installed on your device.
-
Open your authenticator application and note the authentication code currently displayed.
-
Enter the authentication code displayed in the authenticator application.
-
Click Log In.
 With a text message (SMS).
With a text message (SMS).
-
Click MFA verification via SMS.
The dialog box updates with boxes for entering the numbers of the authentication code, and the ESO Suite sends an authentication code to the phone number recorded in your PM records and identified with MFA codes.
-
Enter the authentication code sent to your MFA-registered phone number.
-
Click Log In.
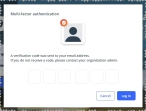
 With an email message.
With an email message.
-
Click MFA verification via email.
The dialog box updates with boxes for entering the numbers of the authentication code, and the ESO Suite sends an authentication code to your agency or department email address, recorded in your PM records.
-
Enter the authentication code sent to your agency or department email address.
-
Click Log In.
-
-
The ESO Suite landing screen appears.
Click graphics
to open them.Note: If MFA is enabled, you can access and manage your MFA options through the PM module, on the Settings > Account page, as described in Manage a user account. If your agency or department has enabled MFA but has not purchased the full-featured version of the PM module, you can access your own MFA settings by clicking Change my Multi-Factor Authentication settings on the landing screen, then using the Settings > Account page that appears. If your agency has not enabled MFA, the Change my Multi-Factor Authentication settings link does not appear on the landing screen.
-
-
On the top side of the home screen, click EHR.
Tip: If your screen or browser window is too narrow to display all your agency's ESO Suite module icons, an options icon appears on the right side of the icon bar. If you click the options icon, a menu appears containing additional module icons.
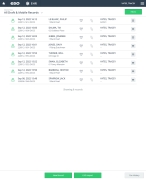
The EHR screen appears, displaying a list of patient records in the EHR module. The most-recent records appear at the top of the list.
Different record status icons can appear in the list.
Icon Status Unlocked/DraftThe patient record exists in the ESO Suite database, and all crew members listed in the patient record may edit all fields in the record. ESO Suite administrators and personnel with security roles of either
EHR SupervisororEHR Managercan edit non-clinical fields.MobileThe patient record exists on the mobile device, and has not been synchronized with the ESO Suite database. ESO Suite administrators, personnel with security roles of either
EHR SupervisororEHR Manager, and all crew members listed in the patient record can only access a print view of the record.Once the Mobile record synchronizes with the ESO Suite database. the record reflects its current status.
LockedThe patient record exists in the ESO Suite database, and is locked. Only non-clinical fields can be edited by crew members listed in the patient record, ESO Suite administrators and personnel with security roles of either
EHR SupervisororEHR Manager.
-
-
 (If you have not done so already) Add a new patient record, or search for the existing patient record you want to work with.
(If you have not done so already) Add a new patient record, or search for the existing patient record you want to work with.
Information on adding or opening a patient record is available in Add a patient record and Search for a patient record.
The patient record opens and displays the Incident tab, with the Response bookmark selected in the left pane. Fields appear in the right pane for specifying basic information about the incident
If you manually created a new patient record, the Incident Number and State Tracking Number fields populate automatically with ESO Suite-assigned values. You must enter data in all other required fields.
If you imported data from a CAD system, the Incident Number field populates with the data from that source. Other fields in the EHR module may also populate from these sources, depending on what data was recorded in them before the data was imported into the EHR module.
-
At the top of the page, click the Forms tab.
The contents of the Forms tab appear, listing all the forms your ESO Suite administrator has enabled in the Admin module.
-
Click Spinal Immobilization Screening Tool.
The Spinal Immobilization Screening Tool dialog box appears.
-
For the following fields, click Yes or No to help evaluate the patient's spinal condition.
Field Information needed Altered Mental Status
An indication of whether the patient displays a mental status ranging from comatose to awake and alert, but confused.
Evidence of Alcohol/Drug Impairment
An indication of whether the patient displays a mental, emotional, or physical impairment from the consumption of alcohol or drugs, and can not exercise reasonable and ordinary control, or readily understand or communicate in spoken language.
Indications of alcohol impairment include lack of coordination, slurred speech, sedation, the smell of alcohol on the patient's breath and/or closing, and a general confused and/or dazed presentation.
Indications of drug impairment include bloodshot eyes, pupils larger or smaller than usual, a runny nose or sniffling, tremors, slurred speech, impaired coordination, unusual odors on breath, body, or clothing, and persistent itching in a specific area of the body.
Distracting Injury
Evidence of a different physical injury that is so severely painful that neck and spinal examination is unreliable.
Example: Severe thoracic trauma, long bone fractures, crush injuries, large burns
Neurologic Deficit
An indication of abnormal function of a body area, including focal deficit, tingling, reduced strength, numbness in extremities, abnormal reflexes, and loss of balance. This altered function is due to injury of the brain, spinal cord, muscles, or nerves.
Spinal Pain/Tenderness
The patient complains of pain or tenderness to the mid-line posterior spine during palpation, and tend to vigorously self-splint.
As you select options for the screening criteria, the indicator in the Immobilization Recommended box of the dialog box updates to a red circle with No in it, or to a green circle with Yes in it, accordingly.
-
Click OK.
The dialog box closes, and a green triangle appears in the upper right corner of the form button, to indicate that data exists in this form.