Specify administration options
The FH Analytics administrator can affect the display of your FIREHOUSE Software data in FH Analytics by specifying the location and type of your FIREHOUSE Software database, the start and end times of your fire department's shift, your unit types, inspection and activity codes, and more.
Caution: Because your FIREHOUSE Software data changes with each incident, inspection, activity, and so forth, you need to periodically choose File → Refresh Data to display the most up-to-date information in FH Analytics. Depending on the size of your FIREHOUSE Software database, it may take a few moments to display the changes in FH Analytics. If your session of FH Analytics appears to be taking more than several minutes to refresh the data, you can choose File → Reopen FH Analytics to restart the application and force a refresh of the data.
The time and date of your most recent data refresh appears in the upper left corner of the screen.
-
Click the Admin tab.
The administration options appears.
-
Depending on the type of FIREHOUSE Software installation you are working with, do one of the following.
 FH Enterprise, using Windows NT authentication
FH Enterprise, using Windows NT authentication
-
Click SQL Integrated.
The SQL Source Data Information information pane appears below the SQL Integrated button.
Note: The vDatabaseType field is display only—you can not change the value in this field.
- In vDatabaseName, enter the name of your FIREHOUSE Software database.
- In vDatabaseServer,enter the name of the database server and the SQL instance name for the FIREHOUSE Software database.
 FH Enterprise, using SQL Server authentication
FH Enterprise, using SQL Server authentication
-
Click SQL DB.
The SQL Source Data Information information pane appears below the SQL DB button.
Note: The vDatabaseType field is display only—you can not change the value in this field.
- In vDatabaseName, enter the name of your FIREHOUSE Software database.
- In vDatabaseServer, enter the name of the database server and the SQL instance name for the FIREHOUSE Software database.
- In vDatabaseUser and vDatabasePassword, enter the username and password of the SQL user with administrative privileges for accessing the FIREHOUSE Software database.
 FH Enterprise, using an ODBC system to access the FIREHOUSE Software database
FH Enterprise, using an ODBC system to access the FIREHOUSE Software database
-
Click ODBC.
The Legacy Source Data Information information pane appears below the ODBC button.
Note: The vDatabaseType field is display only—you can not change the value in this field.
ODBC (Open Database Connectivity) provides a standard software interface for accessing database management systems, independent of database systems and operating systems.
- In vODBCName, type the name of the database management system.
-
-
Under Day / Night Hour Start, for Day Start Hour and Day End Hour, click to the right of the equal sign and enter the hour (on a 24-hour clock) that your fire department's day begins and ends, respectively.
Example: If the fire department's day begins at 6:00 a.m. and ends at 6:00 p.m., in Day Start Hour you would enter
6, and in Day End Hour you would enter18. - Under Use 24 Hour Shifts, in Use 24 Hr Shift, click to the right of the equal sign and enter a Y to indicate that you are using a 24-hour shift, or enter an N to indicate that you are not.
-
(If you entered a
Yin Use 24 Hr Shift) In Shift Start Time, click to the right of the equal sign and enter the time the 24-hour shift starts.Example: If you enter
7, the reports start at 7:00 a.m., and go through 6:59:59 a.m. for the next morning. If you enter13, the reports start at 1:00 p.m., and go through 12:59:59 p.m. for the next day. -
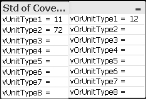
Under Std of Coverage Unit Type, for each type of unit in your FIREHOUSE Software database, in the first column, click to the right of the equal sign and enter the type code for the unit.
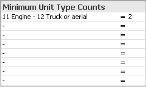
Note: If the unit type should have more than one type code, in the second column, enter the additional type code. FH Analytics creates a logical OR between the type codes. On the Compliance → Standard of Cover tab, in the lower left corner of the interface, under Minimum Unit Type Counts, the name of the unit type is a combination of the two type codes, and you can enter a total number of units for all vehicles of those type codes.
Example: On the Admin tab, under Std of Coverage Unit Type, for vUnitType1 you entered
11, and for vOrUnitType1 you entered12. FH Analytics recognizes that both of type codes 11 and 12 refer to UnitType1.On the Compliance → Standard of Cover tab, in the lower left corner of the interface, under Minimum Unit Type Counts, the name of the unit type listed is 11 Engine - 12 Truck or aerial, and you can enter a total number of units for all your vehicles of type codes 11 and 12.
Note: As a reference, all of the unit types defined in your FIREHOUSE Software database are listed under Unit Type Available. If the list is longer than the available space under Unit Type Available, the list of unit types wraps into a second or third column.
-
Under Inspection Activity Codes, in vInspectionActivityCodes, click to the right of the equal sign and enter the lookup code you set up in FIREHOUSE Software for your inspection activities.
The results of this setting are visible on the Staffing tab, in the Staff Hours sub-tab, when you select the Staff Activity Journal Summary data view for the information pane. In this information pane, you can view the total number of hours a person has worked on inspections.
- Under Max Travel Time Limit, in vMaxTravelTime, click to the right of the equal sign and enter the number of minutes to display on the Compliance tab, on the Compliance sub-tab, on the Travel Time Minutes slider.
-
Under Max Travel Time Limit, in vStaticStep, click to the right of the equal sign and type the number of minutes to add tick marks for on the following information panes.
- On the Compliance tab, Dashboard sub-tab, the Travel Time Mins - All Units information pane.
-
On the Compliance tab, Compliance sub-tab:
- Travel Time Mins - All Units information pane
- 1st Unit Arrival Compliance (Minutes) information pane
- 2nd Unit Arrival Compliance (Minutes) information pane
-
Under Max Response Time Limit, for vMaxResponseTime, click to the right of the equal sign and then type the maximum response time to be allowed when calculating incident compliance values for unit responses.
By filtering out aberrant response times, you can get a more accurate picture of your typical response times.
- Under Use Dispatch Time, in vUseDispatchTime, click to the right of the equal sign and enter a Y to start the response timer from the time of the received 911 call, or enter an N to start the response timer from the alarm time.
-
Under Scramble Patient, in vScramblePatient, click to the right of the equal sign and enter a Y to conceal (scramble) the names of patients when displayed in FH Analytics, or enter an N to display the names of patients in FH Analytics.
The results of your setting appears on the EMS tab, in the Patient Information by information pane, when you select the Patient Data data view.
-
Under Tab Pointers, click to the right of the equal sign and enter either
0or1to hide or display the corresponding tab in the FH Analytics interface.This feature can be useful if you do not have a particular module in FIREHOUSE Software, and do not want to display its corresponding tab in FH Analytics.
Example: If you do not use the Occupancy module in FIREHOUSE Software, you can hide the Occupancies tab in the FH Analytics interface by clicking vTabOccupancies and entering
0. - (Optional) Click Reset Tabs to reset the values under Tab Pointers to their default values.
-
Under Color Selections, for both Selected Button and UnSelected Button, click to the right of the equal sign and enter a value between 0–255 for each of the red, green, and blue color saturation values of selected and unselected buttons on the FH Analytics interface.
Example: To change the color of selected buttons in the FH Analytics interface from a light grey to a primary red, you would click to the right of the equal sign and enter 255 for the first value (red), 0 for the second value (green), and 0 for the third value (blue), so that the field contains
RGB(255,0,0). -
(Optional) For any of the Incident Type fields, click to the right of the equal sign, and type
RGB(, a value between 0–255 for each of the red, green, and blue color saturation values you want to use, and then type)to represent different categories of incidents.Example: To change the color of Incident Type 1 (fire incidents) from their current color assignment to purple, you would enter
RGB(153,0,153).The Incident Type colors represent the following categories of incidents:
- Incident Type 1 = Fire (100-series incident codes)
- Incident Type 3 = EMS (300-series incident codes)
- Incident Type 4 = Hazmat (400-series incident codes)
- Incident Type 7 = False (700-series incident codes)
- Incident Type X = Other (Any other series of incident codes)
- (Optional) Click Reset Colors to reset the values under Color Selections to their default values.
-
Under New Release, in vNewRelease, click to the right of the equal sign and enter a Y to indicate that FH Analytics should use the default settings of a new release when you install it, or an
Nto indicate that it should load the settings you defined in your previous version of FH Analytics.Warning: This feature is not currently implemented in FH Analytics. The New Release section is a place holder on the interface for future development work.
-
Under Fiscal Year Start, in vFiscalYearStart, click to the right of the equal sign and enter the number of the month the fiscal year starts in.
Example: If your fiscal year starts in March, you would enter
3.The calendar interface on the other tabs in FH Analytics starts with the month you specify, instead of with January, and the labels in the calendar interface update accordingly to Fiscal Year and Fiscal Period.
Note: If you enter
0, the calendar interface on other tabs reflects a normal (non-fiscal) year, and the labels in the calendar interface are Year and Month. -
Under Min Data Year, in vMinDataYear, click to the right of the equal sign and enter the oldest year you to want use when analyzing data from the FIREHOUSE Software database.
Example: Your FIREHOUSE Software database contains records from 1995 to the present, but you only need to analyze the data from 2007 to the present. If you enter 2007 for vMinDataYear, only the records from the 2007 to the present are analyzed in FH Analytics.
Note: By default, 2010 is the minimum data year. If you want to analyze records pre-dating 2010, you need to change this value.
- Choose File → Refresh Data.